This is an advanced guide that assumes you already have a working text-based LLM application.
If you are starting from scratch, see the Quickstart guide.
Change baseURL to C1
The first step is to change the OpenAI SDK instantiation to point to C1 rather than the default OpenAI endpoint.
This change is generally only required in one place in your application - where you instantiate the Gateway LLM
(the first LLM that is invoked when the user interacts with your application).And then change the model name to use one of the supported models.Once you’ve done this successfully, you will be able to see your application rendering Thesys DSL responses as plain text.
Add the C1Component to your application
Now that we are able to see the DSL responses, we can add the C1Component to our application to render the DSL responses as a live UI.First, install the necessary packages for C1 integration:Now simply replace the At this point, you should be able to see your application rendering the DSL responses as a live micro-frontend.
Markdown component with the C1Component component.(Optional) Streaming the responses
To improve the user experience, you can stream the responses from the backend to the frontend.
This reduces the perceived latency of the application and makes it feel more responsive.You can easily implement this by storing
<C1Component /> supports streaming the responses and progressively rendering the UI by passing the isStreaming prop.
This prop should be set to true when the response is being streamed and false when the response is done streaming.isStreaming as a state variable that is set to true when the fetch
request is made and set to false when the request is complete.At this point, you should be able to see your application streaming the responses and progressively rendering the UI.Enabling interactivity
At this stage, you should be able to see the application rendering buttons and forms but they won’t be functional.
In order to make them functional, you need to pass the It is important to have the distinction to improve the user experience. The
onAction callback to the C1Component and implement the logic to handle the action.In most cases, you will want to treat the onAction callback as a way to trigger the next turn of the conversation.
This means it will function as if the user had typed in a query and hit enter.llmFriendlyMessage would not be suitable for humans to read in most cases.
Your message store probably won’t have the llmFriendlyMessage in it but in the long term, it is a good idea to store it in the message store.Once you’ve implemented this all the buttons and forms should be functional.Saving form values
While your chat interface is working, the form values don’t persist when you refresh the page.
This is because the form values are also stored in the Once you’ve implemented this, you should be able to see UI generations, have functional buttons and forms and
the form values would persist when you refresh the page.
c1Response object. To enable persistence,
you can pass the updateMessage callback to the C1Component and implement the logic to persist the form values.Typically PUT or PATCH requests are used to update the message in the database.
You might have to implement this endpoint in your backend if it’s not already implemented.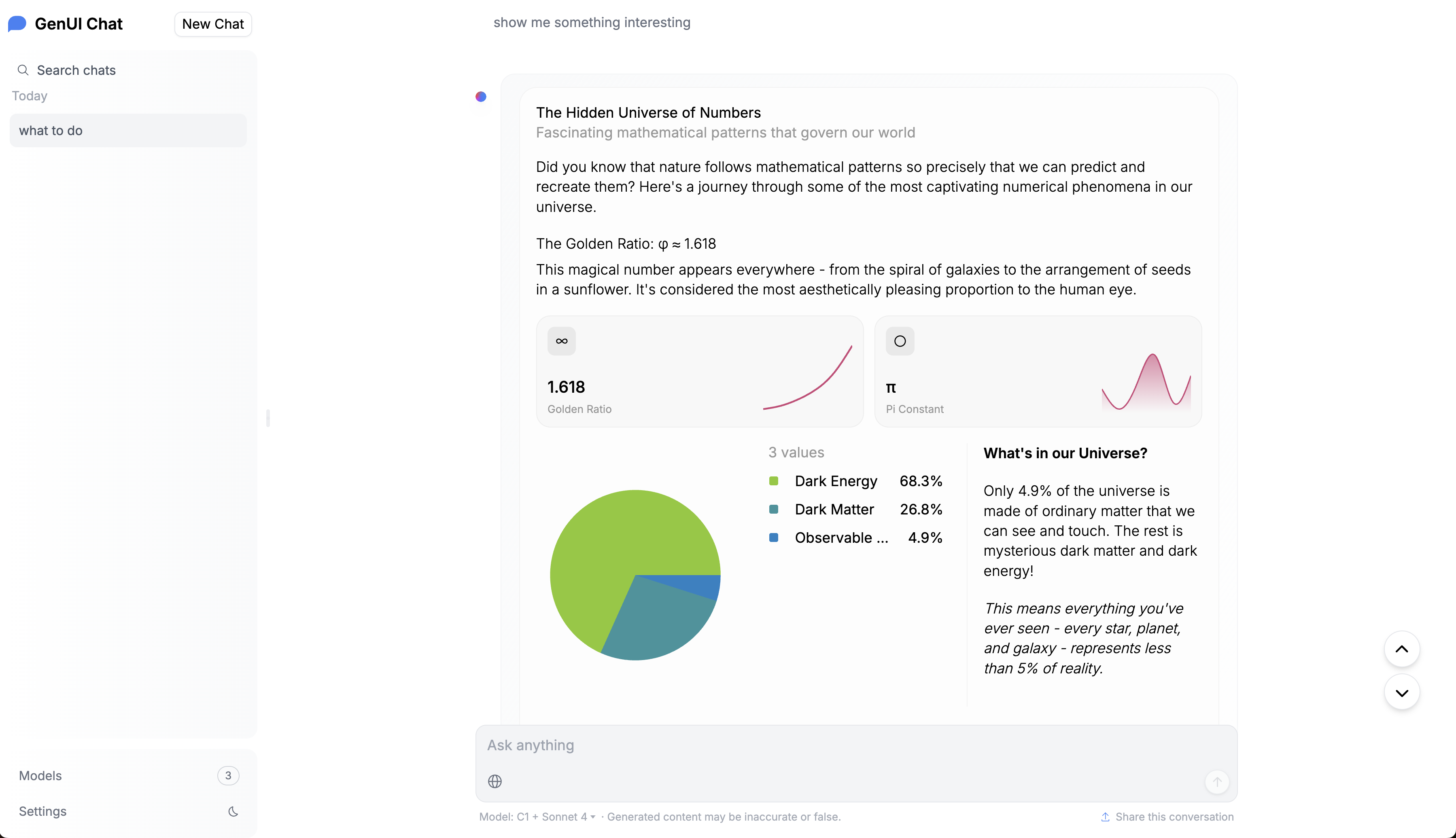
Migrating to GenUI
C1Component is a powerful abstraction that can be used to embed Generative UI within your application.
Above is a screenshot of a fork of HuggingFace Chat UI integrated with C1Component